
The perfect all-round plastic for your prototyping needs. PETG is a popular 3D printer filament. The ‘G’ stands for “glycol-modified”, and the result is a filament which is clearer, less brittle, and most importantly, easier to use than its base form. For this reason, PETG is often considered a good middle ground between ABS and PLA, the two most commonly used 3D printer filaments, as it is more flexible and durable than PLA and easier to print than ABS.
The material is strong and extremely versatile, easy to paint and post process making it the perfect choice for almost any 3D printing project.
PETG CHARACTERISTICS:
Tolerances: ±0.5% with a lower limit of ±0.5 mm (±0.020″)
Max Part Size: 450 x 450 x 470 mm
Layer Height: 100 – 300
Infill Options: 20% Standard – 80-100% High Infill
Wall Thickness: 0.8 mm
Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
Low-cost, fast turnaround times | Limited dimensional accuracy, print layers are likely to be visible
|
PETG is a good all-rounder but stands out from many other filaments due to its flexibility, strength, and temperature and impact resistance. This makes it an ideal 3D printer filament to use for objects which might experience sustained or sudden stress, like mechanical parts, printer parts, and protective components.
RECOMMENDED FOR:
✔ Fit & Form Testing
✔ Functional Prototypes
✔ Electronic Enclosures and Cases
✔ Large Models
✔ End User Products
✔ Batch Manufacturing
✔ Jigs and Fixtures
✔ Architectural Models
NOT SUITABLE FOR:
✘ Jewellery Design
✘ Small and Detailed Art Models (eg. Miniatures and Gaming)
✘ Designs with Large Curved Surfaces (eg. Spherical Objects)
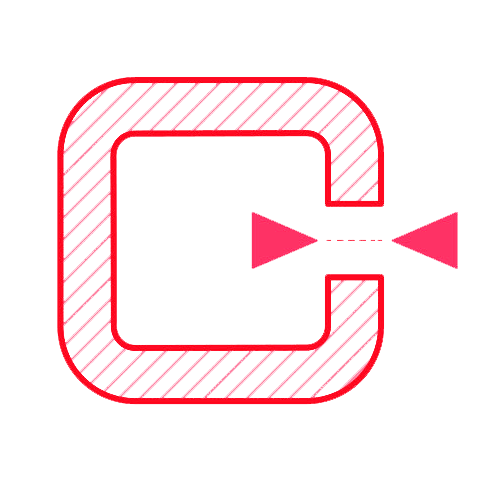
≥ 0.6 mm
Vertical features are often overlooked but they play a very important part in whether or not your print will be successful and how strong the final result will be. We always recommend designing walls with a thickness of at least 1 mm with a minimum viable thickness of 0.6 mm.
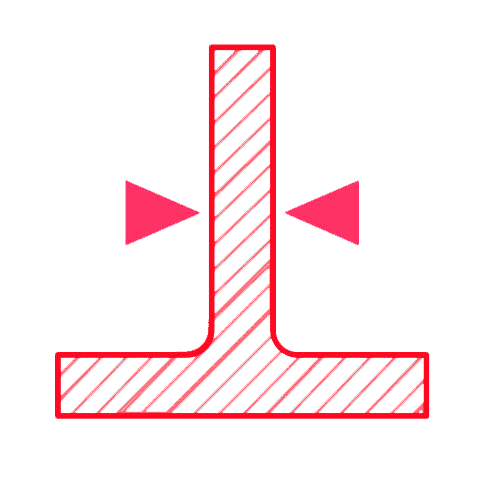
≥ 1.6 mm
In order to achieve the best results we recommend a minimum thickness of 0.6 mm for unsupported walls.
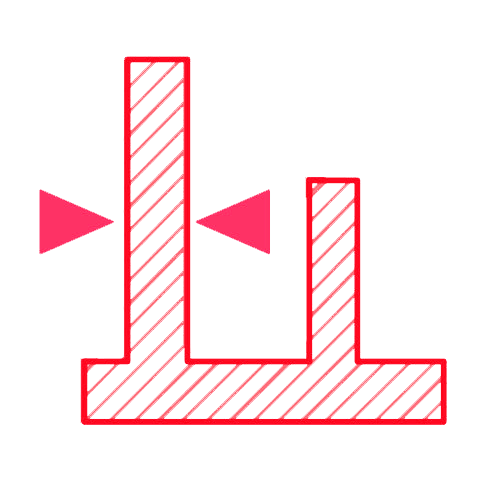
≥ 3 mm
Pins and columns are often used in electronic and end product casings. For best results avoid designing pins with a diameter smaller than 3 mm.
TIP: Adding a chamfer or fillet at the base of your pins will result in much stronger parts.
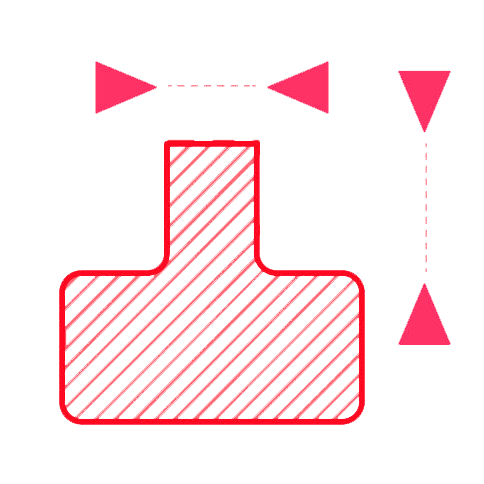
≥ 1.6 mm Thickness
≥ 0.5 mm Depth
Embossed details should have a minimum line thickness of 1.6 mm and a depth of 0.5 mm or higher.

≥ 1.2 mm Thickness
≥ 0.3 mm Depth
Engraved details require a minimum line thickness of 1.2 mm and a depth of at least 0.3 mm.
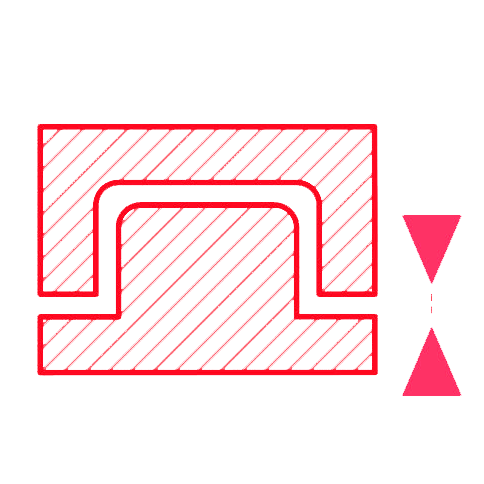
≥ 0.4 mm
When designing an assembly of parts we suggest leaving a clearance of at least 0.4 mm around moving/sliding parts.
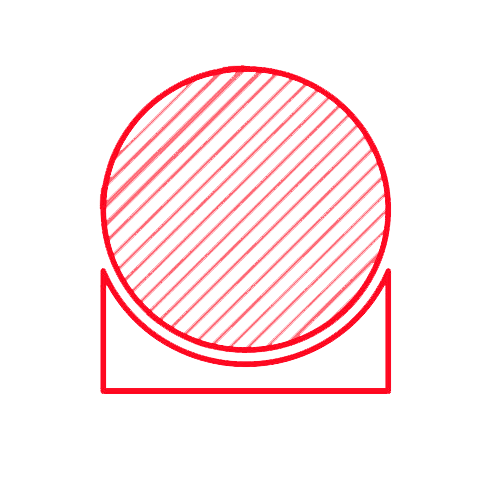
Our PLA / PETG / ABS / PC requires supports in order to print overhanging areas. It’s important to keep this in mind during the design phase since the surface in contact with the support material will exhibit a rougher finish compared with the rest of the model.
SLA 3D Printing material
FDM 3D Printing material
1. Strength and Durability
2. Chemical and Moisture Resistance
3. Ease of Use
4. Versatile Applications
PETG’s balance of properties makes it suitable for:
PETG has limited dimensional accuracy compared to more rigid materials like PLA.
Additional post-processing steps, such as sanding and chemical smoothing, may be necessary to achieve a smooth surface.
PETG is used for creating durable, impact-resistant parts and prototypes.
Strength and ease of use make PETG ideal for manufacturing casings and functional components.
These industries leverage PETG’s robustness and chemical resistance for various applications, including mechanical parts and protective gear.
PETG’s safety and versatility make it ideal for creating functional models and hands-on learning aids in STEM education.
PETG’s ability to withstand environmental conditions extends its industrial relevance for outdoor use.
Sanding can smooth out layer lines and create a more polished surface.
PETG can be painted, and its chemical resistance means it can be treated with various paints without degrading.
Using solvents like dichloromethane can enhance surface smoothness.
PETG can be glued using standard adhesives, facilitating the assembly of complex multi-part models.
PETG is fully recyclable, contributing to reduced waste and supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
The production of PETG generates fewer emissions and consumes less energy compared to some other plastics.
PETG’s durability and long lifespan mean parts are less likely to need frequent replacement, reducing the environmental impact.
PETG is known for its high print quality and smooth surface finish.
Excellent layer adhesion ensures strong, cohesive prints with minimal warping.
Prints have a glossy appearance, and while layers may be visible, they are typically less pronounced than with some other materials.
PETG is available in transparent variants, suitable for applications where clarity is essential.
The inherent strength and durability of PETG, combined with its transparency, provide an excellent solution for applications requiring both visibility and robustness.
Yes, PETG can be used for high-speed printing, though achieving the best results requires careful optimization of printer settings.
By fine-tuning these parameters, PETG can produce high-quality prints efficiently, making it suitable for rapid prototyping and batch manufacturing.
Yes, PETG is compatible with dual extrusion 3D printing, enabling the creation of multi-material or multi-color prints.
Dual extrusion with PETG can be used for advanced 3D printing projects, including: